Description
The BMP180 is a popular digital barometric pressure and temperature sensor developed by Bosch Sensortec.
It is designed to measure atmospheric pressure, temperature, and altitude with high accuracy and resolution.
The BMP180 uses a piezo-resistive pressure sensor and a temperature sensor to provide accurate measurements of atmospheric pressure and temperature.
The pressure sensor measures the absolute pressure of the air, and the temperature sensor compensates for temperature variations.
The BMP180 then uses these measurements to calculate the altitude above sea level.
The module uses an I2C communication protocol for communicating with the microcontroller.
BMP180 Module Specification
Pressure range: 300hPa to 1100hPa and resolution of 0.1hPa.
Altitude range: -500 m to 9000 m with a resolution of 0.1m (0.328 ft).
Accuracy: ±1hPa for pressure and ±1°C for temperature and ±1 meter under normal conditions.
Temperature range: -40°C to +85°C
Interface: I2C upto 3.4MHz
Supply voltage: 1.8 V to 3.6 V
BMP180 Pinouts
BMP180 Pin Description
VCC: Connected to the positive supply of 3.3V
GND: Common Ground pin.
SCL: Serial Clock Line pin for I2C communication.
SDA: Serial Data pin for I2C communication.
BMP180 Hardware Connection with NodeMCU
Extracting Data from BMP180 using NodeMCU
Reading the values from BMP180 and displaying them on the Arduino IDE’s serial monitor.
Here, we'll make use of Adafruit’s BMP180 library named Adafruit_BMP085.h
We will download it from the library manager of Arduino IDE.
Now open an example of Adafruit ADXL345 io dashboard. To open it navigate to File ->Examples -> Adafruit BMP180 Library-> BMP085test
Code for reading values and display it on the Serial Monitor
#include <Adafruit_BMP085.h>
/***************************************************
This is an example for the BMP085 Barometric Pressure & Temp Sensor
Designed specifically to work with the Adafruit BMP085 Breakout
----> https://www.adafruit.com/products/391
These pressure and temperature sensors use I2C to communicate, 2 pins
are required to interface
Adafruit invests time and resources providing this open source code,
please support Adafruit and open-source hardware by purchasing
products from Adafruit!
Written by Limor Fried/Ladyada for Adafruit Industries.
BSD license, all text above must be included in any redistribution
****************************************************/
// Connect VCC of the BMP085 sensor to 3.3V (NOT 5.0V!)
// Connect GND to Ground
// Connect SCL to i2c clock - on '168/'328 Arduino Uno/Duemilanove/etc thats Analog 5
// Connect SDA to i2c data - on '168/'328 Arduino Uno/Duemilanove/etc thats Analog 4
// EOC is not used, it signifies an end of conversion
// XCLR is a reset pin, also not used here
Adafruit_BMP085 bmp;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
if (!bmp.begin()) {
Serial.println("Could not find a valid BMP085 sensor, check wiring!");
while (1) {}
}
}
void loop() {
Serial.print("Temperature = ");
Serial.print(bmp.readTemperature());
Serial.println(" *C");
Serial.print("Pressure = ");
Serial.print(bmp.readPressure());
Serial.println(" Pa");
// Calculate altitude assuming 'standard' barometric
// pressure of 1013.25 millibar = 101325 Pascal
Serial.print("Altitude = ");
Serial.print(bmp.readAltitude());
Serial.println(" meters");
Serial.print("Pressure at sealevel (calculated) = ");
Serial.print(bmp.readSealevelPressure());
Serial.println(" Pa");
// you can get a more precise measurement of altitude
// if you know the current sea level pressure which will
// vary with weather and such. If it is 1015 millibars
// that is equal to 101500 Pascals.
Serial.print("Real altitude = ");
Serial.print(bmp.readAltitude(101500));
Serial.println(" meters");
Serial.println();
delay(500);
}
Now upload the code.
After uploading the code open the serial monitor and set the baud rate to 9600 to see the output.
Output on the serial monitor
Let’s understand the code
In the beginning, we imported the library of BMP180.
Adafruit_BMP085.h library has all the functions and classes for extracting the data from the module.
#include <Adafruit_BMP085.h>Now we created an object for Adafruit_BMP085 class as bmp
Adafruit_BMP085 bmp; In the setup function, we have defined the baud rate to 9600.
Now, we have used an if condition to check if the module is connected or not using begin() function.
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
if (!bmp.begin()) {
Serial.println("Could not find a valid BMP085 sensor, check wiring!");
while (1) {}
}
}In the loop function, we have extracted the data from the module using functions such as read Temperature(), readPressure(), readAltitude(), and readSealevelPressure().
The data is extracted using these functions and displayed the values on the serial monitor one by one repeatedly.
Serial.print("Temperature = ");
Serial.print(bmp.readTemperature());
Serial.println(" *C");
Serial.print("Pressure = ");
Serial.print(bmp.readPressure());
Serial.println(" Pa");
Serial.print("Altitude = ");
Serial.print(bmp.readAltitude());
Serial.println(" meters");
Serial.print("Pressure at sealevel (calculated) = ");
Serial.print(bmp.readSealevelPressure());
Serial.println(" Pa");
Serial.print("Real altitude = ");
Serial.print(bmp.readAltitude(101500));
Serial.println(" meters");
Serial.println();
delay(500);
BMP180 Barometer Sensor over NodeMCU Web Server
Let’s interface the BMP180 to NodeMCU and display the data on the web server as well as on the serial monitor.
Before uploading the code make sure you have added your SSID and Password as follows.
const char* ssid = "*Your SSID*"; /*Enter Your SSID*/
const char* password = "*Your Password*"; /*Enter Your Password*/BMP180 Webserver Code for NodeMCU.
#include <Adafruit_BMP085.h>
#include <ESP8266WebServer.h>
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include "html.h"
ESP8266WebServer server(80);
Adafruit_BMP085 bmp;
int temperature,pressure,altitude,sea_level_pressure,real_altitude;
const char* ssid = "*Your SSID*"; /*Enter Your SSID*/
const char* password = "*Your Password*"; /*Enter Your Password*/
void MainPage() {
String _html_page = html_page; /*Read The HTML Page*/
server.send(200, "text/html", _html_page); /*Send the code to the web server*/
}
void bmp180() {
String data = "[\""+String(temperature)+"\",\""+String(pressure)+"\",\""+String(altitude)+"\",\""+String(sea_level_pressure)+"\",\""+String(real_altitude)+"\"]";
server.send(200, "text/plane", data);
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA); /*Set the WiFi in STA Mode*/
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
delay(1000); /*Wait for 1000mS*/
while(WiFi.waitForConnectResult() != WL_CONNECTED){Serial.print(".");} /*Wait while connecting to WiFi*/
Serial.print("Connected to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
Serial.print("Your Local IP address is: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); /*Print the Local IP*/
server.on("/", MainPage); /*Display the Web/HTML Page*/
server.on("/readBMP180", bmp180); /*Display the updated data*/
server.begin(); /*Start Server*/
delay(1000); /*Wait for 1000mS*/
if (!bmp.begin()) {
Serial.println("Could not find a valid BMP085 sensor, check wiring!");
while (1) {}
}
}
void loop() {
server.handleClient();
temperature = bmp.readTemperature();
Serial.print("Temperature = ");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.println(" *C");
pressure = bmp.readPressure()/100.0F;
Serial.print("Pressure = ");
Serial.print(pressure);
Serial.println(" Pa");
altitude = bmp.readAltitude();
Serial.print("Approx altitude = ");
Serial.print(altitude); /* Adjusted to local forecast! */
Serial.println(" m");
sea_level_pressure = bmp.readSealevelPressure()/100.0F;
Serial.print("Pressure at sealevel (calculated) = ");
Serial.print(sea_level_pressure);
Serial.println(" Pa");
real_altitude = bmp.readAltitude(101500);
Serial.print("Real altitude = ");
Serial.print(real_altitude);
Serial.println(" meters");
Serial.println();
delay(2000);
}
Now, upload the code in NodeMCU and open Serial Monitor.
Set the baud rate to 9600.
Now open any internet browser on your mobile or computer and type the IP address shown on the serial monitor.
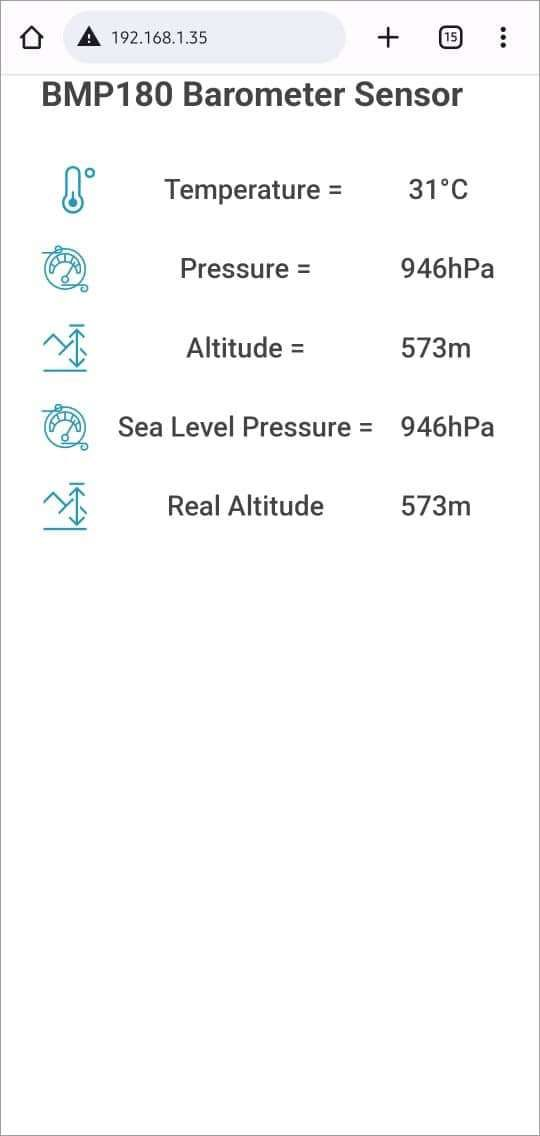
Then hit the enter button, if everything goes all right, the webpage will start showing the temperature, pressure, and altitude.
Note: Ensure that the nodemcu and the device on which you are using the internet browser are connected to the same server/router. If it is not connected to the same broadband then the webpage will not be seen.
Final Output on Webserver
Let’s Understand the Code
Next is the Adafruit_BMP085.h which includes functions for reading temperature and pressure values from the sensor and configuring its settings.
The ESP8266WebServer.h helps in creating the web server on ESP8266 and provides functions for handling incoming HTTP requests and sending responses back to the client.
ESP8266WiFi.h includes the functions that connect the microcontroller to the Wi-Fi network and html.h library has the webpage code.
Now we set the HTTP port as Port 80,
ESP8266WebServer server(80);
In the Setup Function
We have set the WiFi as STA Mode that is the device will connect to the WiFI network as a client.
Using the function WiFi.begin() we connect the microcontroller to the given SSID and Password.
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA); /*Set the WiFi in STA Mode*/
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
delay(1000); /*Wait for 1000mS*/
while(WiFi.waitForConnectResult() != WL_CONNECTED){
Serial.print(".");} /*Wait while connecting to WiFi*/
Serial.print("Connected to ");
Serial.println(ssid);After the successful connection of the server, the local IP address is printed on the serial monitor.
Serial.print("Your Local IP address is: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP())}; /*Print the Local IP*/
Handling Client Requests and Serving the WebPage
The function server.on() sets the request handler for the root directory of the web server.
When the client sends the request to the root (/), MainPage() function is called.
Similarly, when the client sends the request to the /readBMP180, the bmp180 function is executed.
And with the begin() function server is started.
server.on("/", MainPage); /*Display the Web/HTML Page*/
server.on("/readBMP180", bmp180); /*Display the updated data*/
server.begin(); /*Start Server*/
Functions Serving HTML
The MainPage() function is used to send an HTTP response to the web server.
The first argument is the HTTP status code, which is 200 in this case, indicating that the request was successful.
The second argument is the content type of the response, which is "text/html" in this case, indicating that the response contains HTML code.
The third argument is the actual content of the response, which is htmlpage, the HTML code for the web page.
void MainPage() {
String _html_page = html_page; /*Read The HTML Page*/
server.send(200, "text/html", _html_page); /*Send the code to the web server*/
}Now, on the other hand, using the function using function bmp180() we send the updated values of temperature, pressure, and altitude to the webpage.
void bmp180() {
String data = "[\""+String(temp)+"\",\""+String(pre)+"\",\""+String(alt)+"\"]";
server.send(200, "text/plane", data);
}In the loop function, the incoming client requests are handled and served to the HTML page with the help of handleclient()
server.handleClient();
HTML Page Code
/*
NodeMCU BMP180 HTML WebServer Code
http:://www.electronicwings.com
*/
const char html_page[] PROGMEM = R"RawString(
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<style>
html { font-family: sans-serif; display: block; margin: 0px auto; text-align: center;color: #444444;}
body{margin: 0px;}
h1 {text-align: center; font-size: 50px;}
.alignment{display: table-cell;vertical-align: middle;position:relative;}
.content{font-weight: 500; font-size: 40px; width: 450px;}
.reading{font-weight: 500; font-size: 40px; padding-right: 25px;}
.finalscript{font-size: 40px;font-weight: 500;position: absolute;top: 14px;}
.data{padding: 20px;}
.box{display: table;margin: 0 auto;}
.symbol{width:75px;}
</style>
<body>
<h1>BMP180 Barometer Sensor </h1><br>
<div class='box'>
<div class='data temp'>
<div class = 'alignment symbol'>
<svg class = 'alignment symbol' viewBox="0 0 32 32" >
<path d="M20.75 6.008c0-6.246-9.501-6.248-9.5 0v13.238c-1.235 1.224-2 2.921-2 4.796 0 3.728 3.022 6.75 6.75 6.75s6.75-3.022 6.75-6.75c0-1.875-0.765-3.572-2-4.796l-0.001-0zM16 29.25c-2.9-0-5.25-2.351-5.25-5.251 0-1.553 0.674-2.948 1.745-3.909l0.005-0.004 0.006-0.012c0.13-0.122 0.215-0.29 0.231-0.477l0-0.003c0.001-0.014 0.007-0.024 0.008-0.038l0.006-0.029v-13.52c-0.003-0.053-0.005-0.115-0.005-0.178 0-1.704 1.381-3.085 3.085-3.085 0.060 0 0.12 0.002 0.179 0.005l-0.008-0c0.051-0.003 0.11-0.005 0.17-0.005 1.704 0 3.085 1.381 3.085 3.085 0 0.063-0.002 0.125-0.006 0.186l0-0.008v13.52l0.006 0.029 0.007 0.036c0.015 0.191 0.101 0.36 0.231 0.482l0 0 0.006 0.012c1.076 0.966 1.75 2.361 1.75 3.913 0 2.9-2.35 5.25-5.25 5.251h-0zM16.75 21.367v-3.765c0-0.414-0.336-0.75-0.75-0.75s-0.75 0.336-0.75 0.75v0 3.765c-1.164 0.338-2 1.394-2 2.646 0 1.519 1.231 2.75 2.75 2.75s2.75-1.231 2.75-2.75c0-1.252-0.836-2.308-1.981-2.641l-0.019-0.005zM26.5 2.25c-1.795 0-3.25 1.455-3.25 3.25s1.455 3.25 3.25 3.25c1.795 0 3.25-1.455 3.25-3.25v0c-0.002-1.794-1.456-3.248-3.25-3.25h-0zM26.5 7.25c-0.966 0-1.75-0.784-1.75-1.75s0.784-1.75 1.75-1.75c0.966 0 1.75 0.784 1.75 1.75v0c-0.001 0.966-0.784 1.749-1.75 1.75h-0z"fill="#2198c0"/></svg></svg>
</div>
<div class='alignment content'>Temperature = </div>
<div class='alignment reading'><span id="temperature">0</span><span class="finalscript">°C</span></div>
</div>
</div>
<div class='box'>
<div class='data temp'>
<div class = 'alignment symbol'>
<svg class = 'alignment symbol' viewBox="0 0 64 64 ">
<path d="M40.9,27.2l-7.6,12.9C32.9,40.1,32.5,40,32,40c-2.8,0-5,2.2-5,5s2.2,5,5,5s5-2.2,5-5c0-1.6-0.8-3-1.9-3.9l7.3-12.4 c2,2.3,3.3,5.2,3.5,8.4c0,0.5,0.5,0.9,1,0.9h3.4c0.5,0,0.8-0.3,1-0.7c0.5-1.7,0.7-3.5,0.7-5.3c0-11-9-20-20-20s-20,9-20,20 c0,1.8,0.2,3.6,0.7,5.3c0.1,0.4,0.5,0.7,1,0.7H17c0.5,0,1-0.4,1-0.9C18.5,29.7,24.6,24,32,24C35.4,24,38.5,25.2,40.9,27.2z M32,48 c-1.7,0-3-1.3-3-3s1.3-3,3-3s3,1.3,3,3S33.7,48,32,48z M25.8,23.3l-2.9-6.7c0,0,0-0.1-0.1-0.1c2.4-1.4,5.2-2.3,8.1-2.5v8 C29.2,22.2,27.4,22.6,25.8,23.3z M33,22v-8c3,0.2,5.7,1,8.1,2.5c0,0,0,0.1-0.1,0.1l-2.9,6.7C36.6,22.6,34.8,22.2,33,22z M49.6,36 h-1.7c-0.3-2.3-1.1-4.4-2.2-6.3l3.6-2.7c0.5,1.6,0.7,3.2,0.7,5C50,33.4,49.8,34.7,49.6,36z M48.6,25.1c-0.1,0-0.2,0.1-0.2,0.1 l-3.9,2.9c-0.3-0.4-0.7-0.8-1.1-1.2l1.4-2.4c0.3-0.5,0.1-1.1-0.4-1.4c-0.5-0.3-1.1-0.1-1.4,0.4l-1.2,2c-0.6-0.5-1.3-0.9-1.9-1.3 l2.8-6.5C45.4,19.6,47.4,22.1,48.6,25.1z M16.1,36h-1.7c-0.3-1.3-0.4-2.6-0.4-4c0-1.7,0.3-3.4,0.7-5l3.6,2.7 C17.2,31.6,16.4,33.7,16.1,36z M19.5,28.1l-3.9-2.9c-0.1-0.1-0.1-0.1-0.2-0.1c1.2-3,3.3-5.5,5.8-7.5l2.8,6.5 C22.2,25.2,20.7,26.5,19.5,28.1z"fill="#2198c0"/>
<path d="M56,51h-6.3c5.1-4.7,8.3-11.5,8.3-19C58,17.7,46.3,6,32,6c-1.1,0-2.2,0.1-3.3,0.2C27.9,4.3,26.1,3,24,3h-1 c-2.2,0-4,1.8-4,4c0,0.8,0.3,1.5,0.8,2c-1.1,0.6-2.1,1.2-3.1,2H4c-0.6,0-1,0.4-1,1s0.4,1,1,1h10.3C9.2,17.7,6,24.5,6,32 c0,14.3,11.7,26,26,26c5.7,0,11-1.9,15.3-5H56c1.7,0,3,1.3,3,3s-1.3,3-3,3h-1c-1.1,0-2-0.9-2-2c0-0.6,0.4-1,1-1c0.6,0,1-0.4,1-1 s-0.4-1-1-1c-1.7,0-3,1.3-3,3c0,2.2,1.8,4,4,4h1c2.8,0,5-2.2,5-5S58.8,51,56,51z M22,8c-0.6,0-1-0.4-1-1c0-1.1,0.9-2,2-2h1 c1.1,0,2.1,0.6,2.6,1.6C25,6.9,23.5,7.4,22,8C22,8,22,8,22,8z M26.9,8.5C26.7,9.9,25.5,11,24,11h-3.6C22.4,9.9,24.6,9,26.9,8.5z M32,56C18.8,56,8,45.2,8,32c0-7.7,3.7-14.6,9.4-19H24c2.7,0,4.9-2.1,5-4.8C30,8.1,31,8,32,8c13.2,0,24,10.8,24,24 c0,7.7-3.7,14.6-9.4,19H28c-0.6,0-1,0.4-1,1s0.4,1,1,1h15.6C40.2,54.9,36.2,56,32,56z" fill="#2198c0"/></svg></svg>
</svg>
</div>
<div class='alignment content'>Pressure = </div>
<div class='alignment reading'><span id="pressure">0</span><span class='finalscript'>hPa</span></div>
</div>
</div>
<div class='box'>
<div class='data temp'>
<div class = 'alignment symbol'>
<svg class = 'alignment symbol' viewBox="0 0 24 24" >
<path d="M22 23H2v-1h20zM16 9.981V8.567l-.5-.501-2.979 2.995L6.5 5 1.983 9.543v1.44L6.5 6.45l5.307 5.33-3.038 3.055.716.716L15.5 9.48zm3 1.593v1.415l3 3.008v-1.416zM21 1h-7v1h7zm-3 18.293V4.707l2.646 2.646.707-.707L17.5 2.793l-3.854 3.853.707.707L17 4.707v14.586l-2.646-2.646-.707.707 3.853 3.853 3.854-3.854-.707-.707z"fill="#2198c0"/></svg></svg>
</div>
<div class='alignment content'>Altitude = </div>
<div class='alignment reading'><span id="altitude">0</span ><span class='finalscript'>m</span></div>
</div>
</div>
<div class='box'>
<div class='data temp'>
<div class = 'alignment symbol'>
<svg class = 'alignment symbol' viewBox="0 0 64 64 ">
<path d="M40.9,27.2l-7.6,12.9C32.9,40.1,32.5,40,32,40c-2.8,0-5,2.2-5,5s2.2,5,5,5s5-2.2,5-5c0-1.6-0.8-3-1.9-3.9l7.3-12.4 c2,2.3,3.3,5.2,3.5,8.4c0,0.5,0.5,0.9,1,0.9h3.4c0.5,0,0.8-0.3,1-0.7c0.5-1.7,0.7-3.5,0.7-5.3c0-11-9-20-20-20s-20,9-20,20 c0,1.8,0.2,3.6,0.7,5.3c0.1,0.4,0.5,0.7,1,0.7H17c0.5,0,1-0.4,1-0.9C18.5,29.7,24.6,24,32,24C35.4,24,38.5,25.2,40.9,27.2z M32,48 c-1.7,0-3-1.3-3-3s1.3-3,3-3s3,1.3,3,3S33.7,48,32,48z M25.8,23.3l-2.9-6.7c0,0,0-0.1-0.1-0.1c2.4-1.4,5.2-2.3,8.1-2.5v8 C29.2,22.2,27.4,22.6,25.8,23.3z M33,22v-8c3,0.2,5.7,1,8.1,2.5c0,0,0,0.1-0.1,0.1l-2.9,6.7C36.6,22.6,34.8,22.2,33,22z M49.6,36 h-1.7c-0.3-2.3-1.1-4.4-2.2-6.3l3.6-2.7c0.5,1.6,0.7,3.2,0.7,5C50,33.4,49.8,34.7,49.6,36z M48.6,25.1c-0.1,0-0.2,0.1-0.2,0.1 l-3.9,2.9c-0.3-0.4-0.7-0.8-1.1-1.2l1.4-2.4c0.3-0.5,0.1-1.1-0.4-1.4c-0.5-0.3-1.1-0.1-1.4,0.4l-1.2,2c-0.6-0.5-1.3-0.9-1.9-1.3 l2.8-6.5C45.4,19.6,47.4,22.1,48.6,25.1z M16.1,36h-1.7c-0.3-1.3-0.4-2.6-0.4-4c0-1.7,0.3-3.4,0.7-5l3.6,2.7 C17.2,31.6,16.4,33.7,16.1,36z M19.5,28.1l-3.9-2.9c-0.1-0.1-0.1-0.1-0.2-0.1c1.2-3,3.3-5.5,5.8-7.5l2.8,6.5 C22.2,25.2,20.7,26.5,19.5,28.1z"fill="#2198c0"/>
<path d="M56,51h-6.3c5.1-4.7,8.3-11.5,8.3-19C58,17.7,46.3,6,32,6c-1.1,0-2.2,0.1-3.3,0.2C27.9,4.3,26.1,3,24,3h-1 c-2.2,0-4,1.8-4,4c0,0.8,0.3,1.5,0.8,2c-1.1,0.6-2.1,1.2-3.1,2H4c-0.6,0-1,0.4-1,1s0.4,1,1,1h10.3C9.2,17.7,6,24.5,6,32 c0,14.3,11.7,26,26,26c5.7,0,11-1.9,15.3-5H56c1.7,0,3,1.3,3,3s-1.3,3-3,3h-1c-1.1,0-2-0.9-2-2c0-0.6,0.4-1,1-1c0.6,0,1-0.4,1-1 s-0.4-1-1-1c-1.7,0-3,1.3-3,3c0,2.2,1.8,4,4,4h1c2.8,0,5-2.2,5-5S58.8,51,56,51z M22,8c-0.6,0-1-0.4-1-1c0-1.1,0.9-2,2-2h1 c1.1,0,2.1,0.6,2.6,1.6C25,6.9,23.5,7.4,22,8C22,8,22,8,22,8z M26.9,8.5C26.7,9.9,25.5,11,24,11h-3.6C22.4,9.9,24.6,9,26.9,8.5z M32,56C18.8,56,8,45.2,8,32c0-7.7,3.7-14.6,9.4-19H24c2.7,0,4.9-2.1,5-4.8C30,8.1,31,8,32,8c13.2,0,24,10.8,24,24 c0,7.7-3.7,14.6-9.4,19H28c-0.6,0-1,0.4-1,1s0.4,1,1,1h15.6C40.2,54.9,36.2,56,32,56z" fill="#2198c0"/></svg></svg>
</svg>
</div>
<div class='alignment content'>Sea Level Pressure = </div>
<div class='alignment reading'><span id="sea_level_pressure">0</span ><span class='finalscript'>hPa</span></div>
</div>
</div>
<div class='box'>
<div class='data temp'>
<div class = 'alignment symbol'>
<svg class = 'alignment symbol' viewBox="0 0 24 24" >
<path d="M22 23H2v-1h20zM16 9.981V8.567l-.5-.501-2.979 2.995L6.5 5 1.983 9.543v1.44L6.5 6.45l5.307 5.33-3.038 3.055.716.716L15.5 9.48zm3 1.593v1.415l3 3.008v-1.416zM21 1h-7v1h7zm-3 18.293V4.707l2.646 2.646.707-.707L17.5 2.793l-3.854 3.853.707.707L17 4.707v14.586l-2.646-2.646-.707.707 3.853 3.853 3.854-3.854-.707-.707z"fill="#2198c0"/></svg></svg>
</div>
<div class='alignment content'>Real Altitude </div>
<div class='alignment reading'><span id="real_altitude">0</span ><span class='finalscript'>m</span></div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
setInterval(function() {
var xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhttp.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (this.readyState == 4 && this.status == 200) {
const text = this.responseText;
const myArr = JSON.parse(text);
document.getElementById("temperature").innerHTML = myArr[0];
document.getElementById("pressure").innerHTML = myArr[1];
document.getElementById("altitude").innerHTML = myArr[2];
document.getElementById("sea_level_pressure").innerHTML = myArr[3];
document.getElementById("real_altitude").innerHTML = myArr[2];
}
};
xhttp.open("GET", "readBMP180", true);
xhttp.send();
},50);
</script>
</body>
</html>
)RawString";
Let’s Understand the HTML Code step-by-step
All the html web pages start with <!DOCTYPE html> declaration, it is to inform the browser about the type of document expected.
<!DOCTYPE html>The html tag is the container of the complete html page which represents the top of the html code.
<html>Now using the style tag, we can define the font, size, color, alignment, add images, etc. on the webpage.
Firstly, we have defined seven CSS classes for the design and layout of the webpage.
<style>
html { font-family: sans-serif; display: block; margin: 0px auto; text-align: center;color: #444444;}
body{margin: 0px;}
h1 {text-align: center; font-size: 50px;}
.alignment{display: table-cell;vertical-align: middle;position:relative;}
.content{font-weight: 500; font-size: 40px; width: 450px;}
.reading{font-weight: 500; font-size: 40px; padding-right: 25px;}
.finalscript{font-size: 40px;font-weight: 500;position: absolute;top: 14px;}
.data{padding: 20px;}
.box{display: table;margin: 0 auto;}
.symbol{width:75px;}
</style>
In the <body> tag, we have applied the layouts and design for the webpage by calling the class in the <div> tag.
The symbols of temperature, pressure, and altitude are nothing but SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) images which are defined inside the <svg> tag
The position of the images is defined in the class and the path of the images is given in the <path> tag.
Last, all the defined classes from the <div> tag are closed using </tag>.
The same code is written for all three results i.e., Temperature, Pressure, and Altitude.
<div class='box'>
<div class='data temp'>
<div class = 'alignment symbol'>
<svg class = 'alignment symbol' viewBox="0 0 32 32" >
<path d="M20.75 6.008c0-6.246-9.501-6.248-9.5 0v13.238c-1.235 1.224-2 2.921-2 4.796 0 3.728 3.022 6.75 6.75 6.75s6.75-3.022 6.75-6.75c0-1.875-0.765-3.572-2-4.796l-0.001-0zM16 29.25c-2.9-0-5.25-2.351-5.25-5.251 0-1.553 0.674-2.948 1.745-3.909l0.005-0.004 0.006-0.012c0.13-0.122 0.215-0.29 0.231-0.477l0-0.003c0.001-0.014 0.007-0.024 0.008-0.038l0.006-0.029v-13.52c-0.003-0.053-0.005-0.115-0.005-0.178 0-1.704 1.381-3.085 3.085-3.085 0.060 0 0.12 0.002 0.179 0.005l-0.008-0c0.051-0.003 0.11-0.005 0.17-0.005 1.704 0 3.085 1.381 3.085 3.085 0 0.063-0.002 0.125-0.006 0.186l0-0.008v13.52l0.006 0.029 0.007 0.036c0.015 0.191 0.101 0.36 0.231 0.482l0 0 0.006 0.012c1.076 0.966 1.75 2.361 1.75 3.913 0 2.9-2.35 5.25-5.25 5.251h-0zM16.75 21.367v-3.765c0-0.414-0.336-0.75-0.75-0.75s-0.75 0.336-0.75 0.75v0 3.765c-1.164 0.338-2 1.394-2 2.646 0 1.519 1.231 2.75 2.75 2.75s2.75-1.231 2.75-2.75c0-1.252-0.836-2.308-1.981-2.641l-0.019-0.005zM26.5 2.25c-1.795 0-3.25 1.455-3.25 3.25s1.455 3.25 3.25 3.25c1.795 0 3.25-1.455 3.25-3.25v0c-0.002-1.794-1.456-3.248-3.25-3.25h-0zM26.5 7.25c-0.966 0-1.75-0.784-1.75-1.75s0.784-1.75 1.75-1.75c0.966 0 1.75 0.784 1.75 1.75v0c-0.001 0.966-0.784 1.749-1.75 1.75h-0z"fill="#2198c0"/></svg></svg>
</div>
<div class='alignment content'>Temperature = </div>
<div class='alignment reading'><span id="temp">0</span><span class="finalscript">°C</span></div>
</div>
</div>
Now, this is the JavaScript that comes under the <script> tag, this is also called a client-side script.
<script>A delay of every 50mS is called using the setInterval() function.
setInterval function()here we are creating the html XMLHttpRequest object
var xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();The xhttp.onreadystatechange event is triggered every time the readyState changes and the readyState holds the status of the XMLHttpRequest.
Now in the below code, the ready state is 4 means the request is finished and the response is ready and the status is 200 which means OK.
if (this.readyState == 4 && this.status == 200) {
const text = this.responseText;
const myArr = JSON.parse(text);Now, we are updating the values of the output from the sensor on the webpage using temp, pre, and alt id
document.getElementById("temp").innerHTML = myArr[0];
document.getElementById("pre").innerHTML = myArr[1];
document.getElementById("alt").innerHTML = myArr[2];Here we used the AJAX method to send the updated values to the server without refreshing the page.
In the below function, we have used the GET method and sent the readBMP180 function which we defined in the main code asynchronously.
xhttp.open("GET", "readBMP180", true);Send the request to the server using xhttp.send(); function.
xhttp.send();Close the script
</script>Close the body
</body>Close the html
</html>Components Used:-









Comments